When choosing windows and doors for a home or building, terms like U-value and K-value often appear in technical specifications. Many users find them confusing, but the truth is simple — U-value and K-value are actually the same thing. Both measure a window’s ability to retain heat. The lower the number, the better the insulation.
This article explains what these values mean, why they matter, and how they guide your window selection across different regions.
What Are U-Value and K-Value?
Think of a window or door as a “thermal barrier” between indoor and outdoor environments.
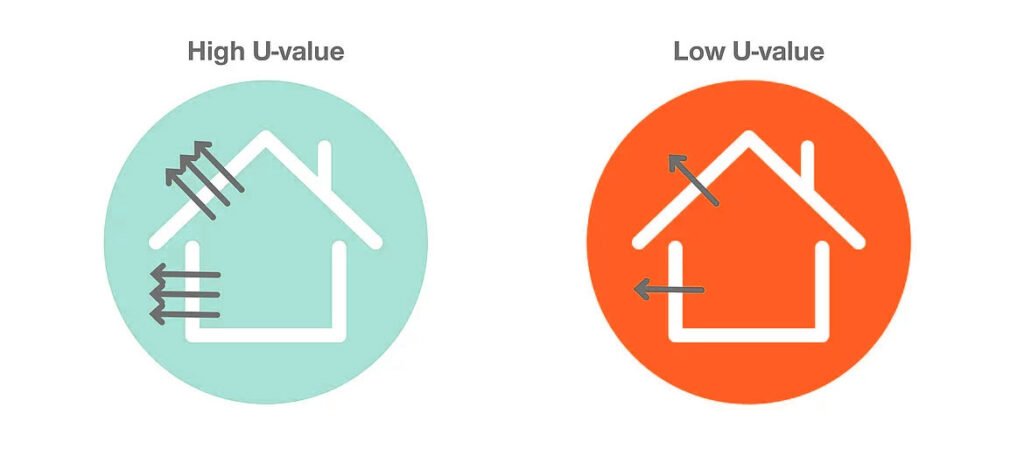
The U/K-value indicates how quickly heat passes through this barrier.
- Lower value = slower heat loss = better insulation
- Higher value = faster heat loss = poorer insulation
For example, in winter, a low U-value helps keep warm air inside; in summer, it helps keep heat outside so you rely less on air conditioning.
Why Should You Care About These Values?
Save Energy Bills
High-performance windows (low U/K-value) reduce the need for heating in winter and cooling in summer.
Improve Comfort
Rooms feel less drafty and cold near windows. Better thermal performance also reduces fogging and condensation on glass.
Meet Building Regulations
Many countries are tightening energy-efficiency requirements. Choosing the correct U/K-value ensures compliance and avoids costly upgrades later.

Typical U/K-Values for Common Window Types
| Window Type | Approximate U/K Value | Performance Level |
| Single glazing | 5.0–6.0 | Very poor insulation |
| Standard double glazing | 2.8–3.5 | Adequate for most homes |
| High-performance triple glazing + Low-E | 1.0–2.0 | Excellent insulation |
A simple rule:
The lower the U-value, the more comfortable and energy-efficient your home will be.

Quick Selection Guide by Region (U/K-Value Requirements)
China — GB/T 8484 Standard
- New regulations (2025) require K ≤ 1.5 in northern heating zones.
- For renovation projects, experts recommend going directly for K ≤ 1.2 for better comfort and energy savings.
United States — ASHRAE / ENERGY STAR
- ENERGY STAR–certified windows can reduce energy usage by 30% or more.
- Some states provide tax credits for high-performance windows.
Europe — EN 14351 Standard
- By 2025, the EU mandates Uw ≤ 1.2 for all new buildings.
- Early adoption helps future-proof your home or building.
Australia — AS 1288 Standard
- Northern regions require cyclone-rated (C4) windows.
- Coastal areas should use materials with high resistance to salt corrosion.
Canada — National Building Code
- Harsh winter regions should prioritize U ≤ 1.0 for maximum insulation.
- Reducing window area may be necessary to achieve ultra-low U-values.

Key Principles for Selecting the Right Windows
Cold / Severe-Winter Climates
- Choose U ≤ 1.0
- Triple glazing and warm-edge spacers are strongly recommended.
Hot / Tropical Climates
- Prioritize low SHGC (≤ 0.4) to block solar heat gain.
- Low-E coatings with selective solar control are ideal.
Humid Regions
- Ensure the window system includes warm-edge spacers + quality desiccants.
- Aim for a glass dew point ≤ 10°C to prevent condensation.
Coastal / Typhoon / High-Wind Areas
- Insulation can be moderately relaxed, but wind-load resistance must be high.
- Recommended: frame thickness ≥ 70 mm, wind pressure resistance ≥ Level 9.

Conclusion
Understanding U-value and K-value is essential for choosing high-performance windows and doors. Although the terms differ across regions, their purpose is the same: to measure how well a window prevents heat loss.
By selecting the right U/K-value based on your climate and building requirements, you’ll enjoy:
- Lower energy costs
- Greater comfort
- Better durability
- Compliance with global efficiency standards
For professional guidance or customized window and door solutions, feel free to contact Delanshini Doors and Windows at wang@gddlsn.com.
